Extensive research has shown that 20% of Indian women deal with Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD). This means that one out of every five women worldwide has PCOD. In this article, we’ll explore the symptoms, treatment, and causes of PCOD.
What is PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease)?
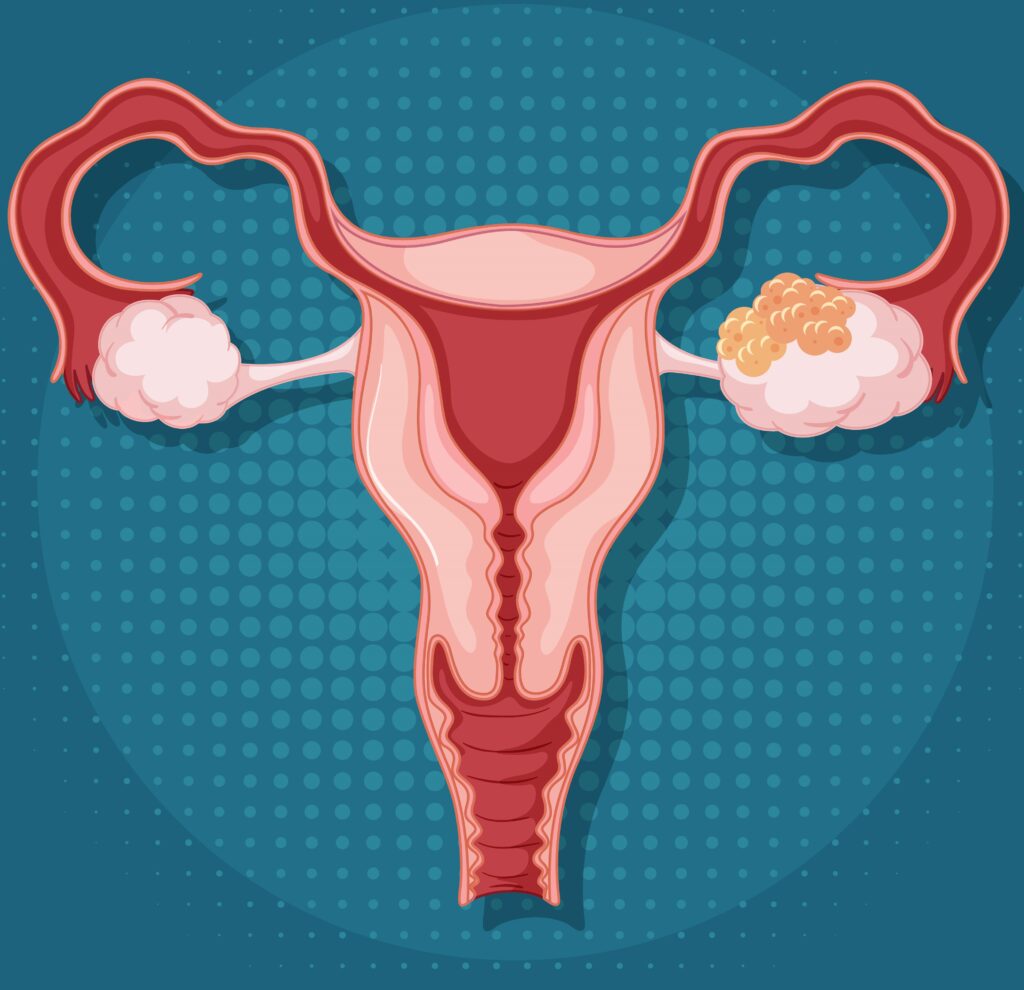
Polycystic Ovarian Disease, or PCOD, is a medical condition that affects women. In PCOD, the ovaries start producing immature eggs that then develop into cysts. This is caused by an increase in male hormones called androgens, which leads to the formation of these follicular cysts. As a result, the release of eggs from the ovaries becomes irregular.
What are the Common PCOD Symptoms?
PCOD can negatively impact the ovaries. Every woman has two ovaries that produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone. The ovaries also release a male hormone called androgen. PCOD disrupts this process, leading to an abnormal release of androgen. Here are some common signs and symptoms of PCOD.
- Irregular Menstrual Periods.
- Heavy Bleeding in Menstrual Cycles.
- Acne.
- Excessive growth of hair on the body.
- Hair Loss.
- Baldness.
- Obesity.
- Pigmentation.
- Sleep Disorder.
- Depression.
What Causes PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease)?
The exact causes of polycystic ovarian disorder (PCOD) are not fully understood. Many medical experts believe PCOD can develop due to both genetic and environmental factors. The condition arises for a variety of reasons.
- Unhealthy diet.
- Inactive lifestyle.
- Pollution.
- Several medications and supplements.
In many instances, PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) tends to run in families, often with a genetic component. However, there are also various other physiological factors that can contribute to the condition. Let’s take a closer look at some of these potential causes:
1 .Insulin production: Insulin is made by the pancreas, a natural hormone that helps control metabolism and blood sugar levels. Research shows that high insulin levels can lead to polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD). When there’s too much insulin in the body, it stimulates excess androgen production, which then causes PCOD.
2. Inflamation: Low grade inflammation can contribute to the development of polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD) in the body. Various autoimmune disorders can also trigger inflammation in the body’s tissues. This can lead to an increase in male hormones, which in turn results in PCOD.
3. High Levels of Androgen: The hormone called androgen is associated with increased body hair, facial breakouts, and skin conditions. When this hormone levels rise, these issues also increase. These bodily changes can ultimately lead to a condition called PCOD.
What are the Treatment options available for PCOD?
PCOD treatment includes medication in addition to lifestyle modifications. Although there isn’t another treatment for this illness, changing your lifestyle can help a lot. Here’s how!
- Healthy Diet : Eating a balanced diet can be beneficial for managing PCOD. Making some dietary adjustments, such as limiting sugar, fatty, and oily foods, can help alleviate the symptoms. This dietary approach can also lower cholesterol levels and provide relief from cardiovascular issues.
- Schedule Your Lifestyle: Women with a more sedentary lifestyle need to make a conscious effort to exercise regularly in order to manage the condition of PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome). Planning out a consistent workout routine is crucial for these women to overcome the challenges posed by PCOD
- Hormonal treatment: If someone is diagnosed with PCOD, it’s best to get a cyclical hormone treatment and other medications to regulate the periodic cycle. This approach can help manage the condition and bring the menstrual cycle back to a healthy pattern. The treatment aims to balance the hormones and address the underlying causes of PCOD, making it an effective way to address the issue.
- Skin Care: An appropriate skin care regimen can help eliminate dark circles, blotches, acne, and allergies to the skin.
Diagnosis of PCOD / PCOS:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is typically diagnosed based on a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination, and specific criteria. Usually, the following actions are performed in order to diagnose PCOS:
- Medical History: The doctor will talk with you about your menstrual cycle, including any irregular periods, excess hair growth, acne, weight changes, or other relevant health issues. They’ll want to understand your full medical history to provide the best care.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be done to check for signs of PCOS, such as extra body hair, acne, and skin changes caused by hormonal imbalances.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are conducted to measure hormone levels, including levels of androgens (male hormones like testosterone), as well as insulin levels and other metabolic markers. These tests provide valuable insights into a person’s overall health and help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about treatment and management strategies.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: A pelvic ultrasound is used to get a clear view of the ovaries. Ovaries affected by Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) often have a distinct appearance with numerous small cysts.
- Diagnostic Criteria: PCOS is identified using specific guidelines. The most frequently used criteria are the Rotterdam guidelines, which require the presence of at least two of the following: irregular menstrual cycles, signs of high androgen levels (such as excess body hair or acne), and polycystic ovaries observed on ultrasound.